Introduction
As we explained it in the Data Structure article, “Graphs algorithms” are used a lot in real-life. They are used to represent networks like you can find in cities, phones or even in Facebook where each person is represented by a node. Each node contains information like the name, the gender, the phone number etc.
It’s basically a finite structure made of nodes and edges.
Dijkstra’s algorithm
In this article we will take a look at one of the most famous Graph algorithm : the Dijkstra algorithm. It is used to find shortest paths between nodes in a graph.

For example, what is the fastest way to go from node A to point G on the following graph ?
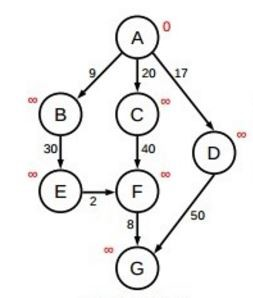
Method
Here is the method to code such algorithm :
- Mark all nodes unvisited and store them.
- Set the distance to zero for our initial node and to infinity for other nodes.
- Select the unvisited node with the smallest distance, it’s current node now.
- Find unvisited neighbors for the current node and calculate their distances through the current node. Compare the newly calculated distance to the assigned and save the smaller one.
- Mark the current node as visited and remove it from the unvisited set.
- Stop, if the destination node has been visited (when planning a route between two specific nodes) or if the smallest distance among the unvisited nodes is infinity. If not, repeat steps 3-6.
Example
Here is a little example of how the algorithm will help us to find the fastest way to go from A to G :
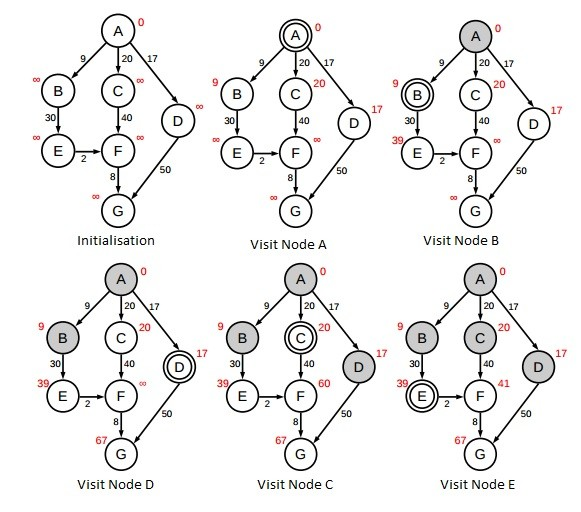
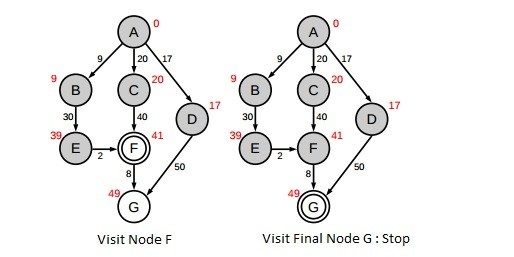
So the fastest way to go to A to G is the following path : A,B,E,F and G with a number of 49 kilometers !
In the next article, we will see together what is hashing !

