VMWare allows you to configure high availability for your virtual machines through vSphere. It means that your VMs will be restarted on alternate hosts if a failure is detected on one of your hosts.
How HA Protection works – Master and Subordinate hosts
HA protects against scenarios such as : host failures, host isolation and application crashes. It is basically handled by splitting monitoring role between a master and subordinate hosts.
As soon as you have configured you cluster, an ESXi is referenced as the master host. This host will be responsible for detecting the failure of subordinate hosts.
The master host in a cluster has several responsibilities:
- Monitoring the state of subordinate hosts. If a subordinate host fails or becomes unreachable, the master host identifies which virtual machines must be restarted.
- Monitoring the power state of all protected virtual machines. If one virtual machine fails, the master host ensures that it is restarted. Using a local placement engine, the master host also determines where the restart takes place.
- Managing the lists of cluster hosts and protected virtual machines.
- Acting as the vCenter Server management interface to the cluster and reporting the cluster health state.
The subordinate hosts primarily contribute to the cluster by running virtual machines locally, monitoring their runtime states (VMWare tools heartbeats), and reporting state updates to the master host.
A master host can also run and monitor virtual machines.
In a vSphere HA cluster, three types of host failure are detected:
- Host failures : a host stop functioning
- Host isolation : a host becomes network isolated
- Application crashes : a host loses network connectivity with the master host
How to configure your HA Cluster
Create a cluster through vSphere with :
- at least 2 ESXis (with licence)
- ESXi using static IPs
- A shared management network
- Access to all networks and datastores
Right click on you cluster and then “Edit settings…”
Turn on vSphere HA and that’s it !
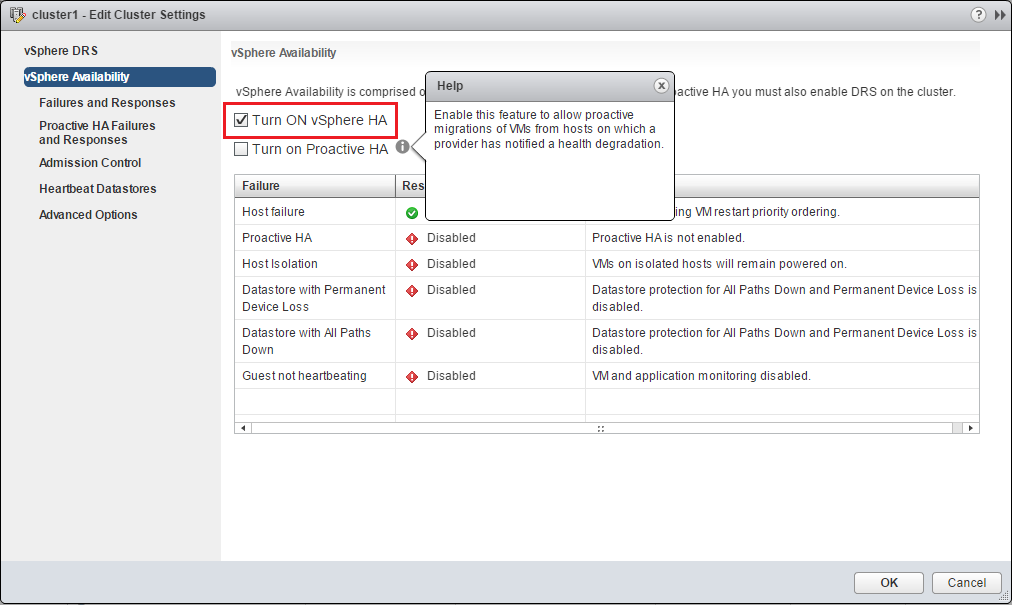
You have successfully created your HA Cluster !
You can now configure it through the following menus as you want :
Failures and responses : Configure how your cluster should function when problems are encountered (host failure responses, host isolation, VM monitoring, and VM Component Protection.)
Proactive HA failures and responses : Provide settings for how Proactive HA responds when a provider has notified its health degradation to vCenter, indicating a partial failure of that host.
Admission Control : Enable or disable admission control for the vSphere HA cluster and choose a policy for how it is enforced (specify whether virtual machines can be started if they violate availability constraints.)
Heartbeat Datastores : Specify preferences for the datastores that vSphere HA uses for datastore heartbeating.
Advanced Options : Customize vSphere HA behavior by setting advanced options.
Sources : vmware.com

